Carbon and its Compound | Solved Questions:
SSLC Science Solved Questions/Model Questions and Answers (Q&A) on the lesson Carbon and its Compounds for the SSLC English Medium students have been updated in this post below. The students of SSLC can make use of this Online Study Package to get good scores in the SSLC examinations.
Teachers also can help the students to access this platform to use this FREE Online Study Package anywhere and any time.
Carbon and its Compounds
One Marks Questions
Answer: 4
Answer: Carboxylic acid
Answer: A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitute for hydrogen in a carbon chain.
Answer: Conc. Sulphuric Acid
Answer: The melting point of pure ethanoic acid is 290K and hence it often freezes during winter in cold climates.
Answer: Alkaline KMnO4 or acidified K2Cr2O7
Answer: Nickel
Answer: 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar.
Answer: Cl/Br
Answer: OH
Answer: (i) Aldehyde group
(ii) Carboxylic acid group

Two Marks Questions

Answer: Compound with identical molecular formula but different structures are called structural isomers.
Eg:

Answer: Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light.
Eg: C+O2 = CO2
Answer:
i) CH3-CH2OH Alkaline KMnO4+Heat CH3COOH
ii)

Answer:
One type of atom or a group of atoms takes the place of another.
CH4+Cl2 = CH3Cl+HCl
Answer:
i) 2Na +2CH3CH2OH=2CH3CH2O-Na++H2
ii)CH3-CH2OH Hot Conc. H2SO4 CH2=CH2+H2O
Answer: 2CH3COOH+Na2CO3 = 2CH3COONa+H2O+CO2 CH3COOH+NaHCO3 = CH3COONa+H2O+CO2
Three and Four Marks Questions
Answer:
i)C3H7OH

ii)C3H6O
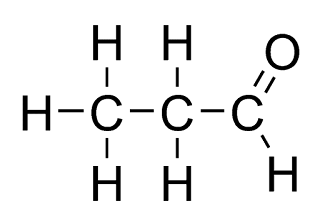
iii) C3H6O

iv)C3H6O2

Answer:
i)

ii)

iii)

iv)

i)The ionic end of soap interact with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecule thus forms a structure called micelles where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplets while the ionic end faces outside. This forms dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean.
ii)
| Soap | Detergents |
|---|---|
| The molecule soap sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. | The sodium salt of sulphonic acids or ammonium salts with chlorides or bromides ions. |
| Form insoluble precipitates in hard water | Do not form insoluble precipitates in hard water |

